The TCFD Recommendations suggest that information has to be disclosed in accordance with the four elements of "Governance," "Strategy," "Risk Management," and "Metrics and Targets" in order to accurately understand how risks and opportunities associated with climate change will impact corporate management, including financials. We will work to enhance information disclosure based on the four items required by the TCFD Recommendations.
We have a Company-wide Sustainability Promotion Committee, which works with the Management and Executive Committee and the Company-wide Environmental Protection Committee to deliberate on policies for climate change-related risks and opportunities. The Board of Directors receives reports on the deliberations of the Company-wide Sustainability Promotion Committee and supervises the progress of initiatives related to climate change issues.
The President/CEO chairs the Company-wide Sustainability Promotion Committee and is ultimately responsible for management decisions on climate change-related issues. The President/CEO receives reports from the Company-wide Environmental Protection Committee and the Company-wide Sustainability Promotion Committee on the Company's response to climate change and progress in addressing climate change issues.
Sustainability Promotion Framework
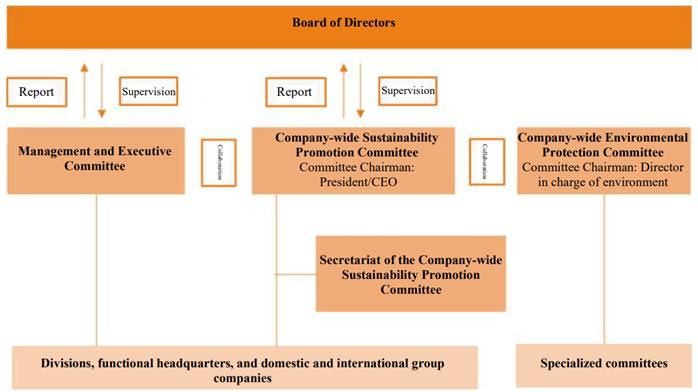
Meeting bodies and roles in the sustainability promotion system
|
Meeting body |
Role and frequency of meetings |
|
Board of Directors |
Supervise the progress of initiatives related to sustainability issues, including climate change-related issues, after the discussion and approval of the business unit (or the Management and Executive Committee). |
|
Company-wide Sustainability Promotion Committee |
Responsible for identifying, assessing, and responding to climate-related risks, and deliberate on measures to key climate-related risks and monitor the progress of such measures. The Committee reports its findings to the Board of Directors. However, the contents has to be confirmed at the Committee with the participation of all members of the Board of Directors. In principle, the Committee takes place four times a year. |
|
Secretariat of the Company-wide Sustainability Promotion Committee |
Identify, evaluate, and manage climate-related risks, and formulate action plans for climate change risks. The results are submitted to the Company-wide Sustainability Promotion Committee. |
|
Company-wide Environmental Protection Committee |
Formulate annual environmental policies in cooperation with the Company-wide Sustainability Promotion Committee and set targets for CO₂ reduction, etc. The Committee also establishes a specialized committee to promote activities for CO₂ reduction. |
|
Management and Executive Committee |
Examine comprehensive risks, including climate change risk, and deliberate and approve countermeasures. The decisions is reported to the Board of Directors on a regular basis. |
We have analyzed climate change related risks and opportunities based on the TCFD recommendations, taking into account short, medium and long-term time perspectives as described below.
Definition of time axis
|
Classification |
期間 |
|
Short-term: |
0-3 years |
|
Medium-term: |
3-10 years |
|
Long-term: |
10-30 years |
We analyzed 1.5°C and 4°C scenarios based on scientific evidence from the International Energy Agency (IEA) and other sources, and evaluated the significance of climate-related risks and opportunities that could affect our business in 2030 (transition risk) and 2050 (physical risk).
Scenario Definition
|
1.5℃scenario |
4℃scenario |
||
|
Scenario Overview |
Climate change measures are aggressively implemented, and government regulations are tightened. As a result, EVs and renewable energies become widespread, and demand for products with high environmental performance expands. |
Climate change response is not implemented, and extreme weather events become more severe. As a result, demand for construction equipment and civil engineering products related to disaster recovery and infrastructure reinforcement expands. |
|
|
Target year |
Transition risk: 2030, Physical risk: 2050 |
||
|
Reference scenario: |
For transition aspects |
IEA NZE*1 |
IEA STEPS*2 |
|
For physical aspects |
IPCC SSP1-1.9*3 |
IPCC RCP8.5*4 |
|
*1 IEA NZE (Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario): A normative scenario presented by the IEA that shows a pathway for the
global energy sector to achieve net zero CO₂ emissions by 2050.
*2 IEA STEPS (Stated Policies Scenario): A conservative scenario presented by the IEA that reflects the policies announced
by national governments.
*3 IPCC SSP1-1.9: A scenario in which CO₂ emissions are reduced to net zero in the middle of the 21st century and the
increase in global average temperature is limited to 1.0-1.8°C (average 1.4°C) compared to the pre-industrial period,
by adopting climate policies that limit the temperature increase to approximately 1.5°C or less, as indicated in the
IPCC's Sixth Assessment Report.
*4 IPCC RCP8.5: A scenario in which the global average temperature at the end of the 21st century (2081-2100) is 3.2-5.4°C
(4.3°C on average) higher than the pre-industrial level, as indicated in the IPCC's Fifth Assessment Report.
List of Risks and Opportunities
|
Types of Risks and Opportunities |
Impact on business |
Time axis |
|
|
Risks |
Policy and Regulation |
・Introduction of carbon tax will increase energy costs and operating costs ・Introduction of carbon tax will increase the price of raw materials such as steel , semiconductors and other goods. ・Introduction of carbon tax will increase fuel prices, and raise transportation costs of raw materials and products ・Greenhouse gas emissions regulations will increase the corresponding costs of installing energy-saving equipment, converting to renewable energy, etc. |
Medium-term: |
|
Market |
・Demand for the parts of gasoline engines will decrease due to the spread of EVs and electric bikes as a result of decarbonization ・Soaring gasoline prices will reduce demand for motorcycles and motorcycle-related products ・Price of steel and other raw materials will rise due to the transition to low carbon emission production process. ・Company’s failure to reduce environmental impact in their business will reduce investor interest and harm their reputation, resulting in a decrease in ESG investment. |
Medium-term: |
|
|
Technology |
・Increased investment costs in production and processing facilities to accommodate decarbonization |
Short-term: |
|
|
Physical (Acute) |
・Opportunity losses and recovery costs will increase due to plant shutdowns caused by severe extreme weather events ・Opportunity losses will be incurred due to stagnation of production when procurement of raw materials becomes difficult due to severe extreme weather events ・Severe extreme weather events can disrupt supply chains, resulting in lost sales opportunities ・Reinforcement cost at plant will increase to avoid infrastructure damage. |
Long-term: |
|
|
Physical (Chronic) |
・The use of air conditioning in office will increase due to rising temperature which resulting in higher electricity costs ・Deterioration of the working environment due to the heat wave will result in a labor shortage and a decrease in sales, which will lead to a decline in revenue ・Water shortages due to global warming will necessitate the cost of investment in water-saving facilities ・Procurement costs for semiconductors will increase due to a shortage of semiconductors caused by increased drought |
Long-term: |
|
|
Opportunities |
Products & Services |
・Demand for high-frequency power supplies used in semiconductor manufacturing will expand because of the spread of renewable energy and EVs ・The shift to EVs will increase demand for products suitable for EV vehicles, as well as demand for components required for the manufacturing process of EV parts ・Demand for high-frequency heat treatment will increase, as it improves product durability and strength and contributes to CO₂ reduction compared to conventional gas carburization ・Demand for high-efficiency high-frequency power supplies will expand in response to rising demand for production and processing equipment that is compatible with decarbonization |
Medium-term: |
|
・Demand for civil engineering-related products will grow as extreme weather events intensify and facilities and infrastructure are strengthened in preparation for disasters ・Demand for construction equipment for disaster recovery will grow as extreme weather events intensify, and demand for construction equipment-related products will also increase |
Long-term: |
||
|
Market |
・High-frequency heat treatment emits less carbon dioxide and consumes less energy than other treatment methods, so the market will expand as an environmentally friendly treatment method ・Policy support for offshore wind power will increase demand for products for wind power generation equipment, including PC steel bars ・Expanding sales opportunities for products for labor-saving and low rebar-loading construction ・Increased ESG investment will draw investor interest and get appreciation when environmental impacts are reduced through business operations |
Medium-term: |
|
Climate-related risks and opportunities of particular importance to us
(Impact assessment criteria)
Large: 500 million yen or more
Medium: 10 million yen or more but less than 500 million yen
Small: less than 10 million yen
|
Risks/Opportunities |
Business Impact |
Financial Impact |
Countermeasures |
|
|
1.5℃ |
4℃ |
|||
|
Risks |
Introduction of carbon tax will increase the price of raw materials such as steel and semiconductors, and raise procurement costs |
Large |
Small |
・Grasp the current situation and set targets ・Increase in recycling rate ・Switch to alternative raw materials |
|
Introduction of carbon tax will increase energy costs, and raise operating costs |
Large (approx. 600 million yen ※1) |
No tax applicable |
・Efforts to save energy and improve productivity ・Switch to renewable energy sources ・Securing electricity in-house by installing solar panels |
|
|
Opportunity losses will be incurred due to stagnation of production when procurement of raw materials becomes difficult due to severe extreme weather events |
Large |
Large |
・Stockpiling of inventories ・Diversification of procurement bases ・Identification of procurement source risk ・Securing multiple purchasing sources |
|
|
Severe extreme weather events can disrupt supply chains, resulting in lost sales opportunities |
Large |
Large |
・Securing multiple means of transportation ・Decentralization of logistics bases ・Adaptation to local procurement |
|
|
Opportunity losses and recovery costs due to plant shutdowns caused by severe extreme weather events will be incurred |
Large (approx. 500 million yen ※2) |
Large (approx. 500 million yen ※2) |
・Decentralization of response ・Infrastructure enhancement |
|
|
Reinforcement cost of infrastructure at plants will increase in response to the high frequency of extreme weather events |
Large |
Large |
・Identification of risks at Group manufacturing plants ・Strengthening physical infrastructure ・Relocate and decentralize people and assets ・Ensure backups |
|
|
Deterioration of the working environment due to a heat wave will result in a labor shortage and a decrease in sales, which will lead to a decline in revenue |
Medium |
Large |
・Improvement of work site environment ・Further promotion of labor saving and other work efficiency improvements |
|
|
Risks/Opportunities |
Business Impact |
Financial Impact |
Countermeasures |
|
|
1.5℃ |
4℃ |
|||
|
Opportunities |
The shift to EVs will increase demand for products suitable for EV vehicles, as well as demand for components required for the manufacturing process of EV parts |
Large |
Small |
・Strengthen supply structure of products for EVs ・Promote development of new technologies (products) |
|
Demand for high-frequency heat treatment will increase, as it improves product durability and strength and contributes to CO₂ reduction compared to conventional gas carburization |
Medium |
Medium |
・Promote development of new technologies (products) ・Promote sales activities for products and services |
|
|
Expanding sales opportunities for products for labor-saving, low rebar-loading construction |
Large |
Medium |
・Expand sales to real estate and construction companies |
|
|
Increased ESG investment will draw interest and get appreciation when environmental impacts are reduced through business operations |
Large |
Medium |
・Strengthen R&D ・Initiatives for internal penetration ・Acquisition of certification ・Promote disclosure |
|
|
Demand for civil engineering-related products will grow as extreme weather events intensify and facilities and infrastructure are strengthened in preparation for disasters |
Medium |
Large |
・Expand sales and strengthen supply system for civil engineering-related products |
|
(Basis for calculation of quantitative financial impact)
*1 Estimated by multiplying the domestic Group Scope 1 and 2 emissions as of 2030 by the carbon price per ton of CO₂.
*2 The maximum amount of damage is estimated. The breakdown is "profit loss due to suspension of operations," "amount of
damage to depreciable assets," and "rate of damage to buildings. Inundation risk for each of the Group's domestic bases is
identified using hazard maps.
Risks related to climate change are being identified and assessed their impact by the Company-wide Sustainability Promotion Committee with the support of the Secretariat. Especially that are deemed urgent and significant ones are reported to the Management and Executive Committee. The Company-wide Sustainability Promotion Committee also works with the Company-wide Environmental Protection Committee to resolve measures to address significant risks and monitor the progress of such measures. The details are reported to the Board of Directors on a regular basis. However, the contents are to be confirmed at the Company-wide Sustainability Promotion Committee with the participation of all members of the Board of Directors.
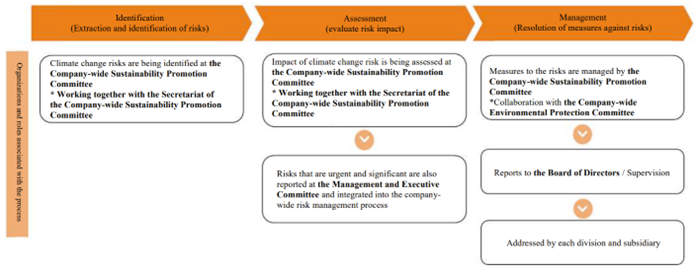
We are calculating greenhouse gas emissions as indicator for assessing climate change-related risks. The calculation covers non-consolidated Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions through FY2022. We have made progress in reducing emissions through the promotion of energy-saving activities to date and have also started initiatives such as the installation of solar power generation systems. We will continue to monitor greenhouse gas emissions, expand the scope of coverage, and implement initiatives to reduce emissions.
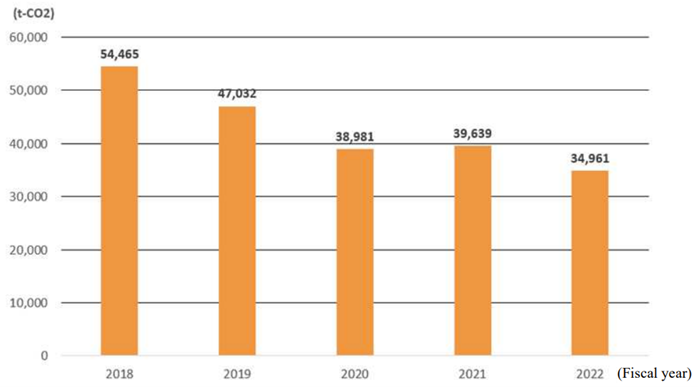
- 拡大
- Changes in CO₂ emissions (Scope 1 and 2 emissions)
*1 Scope 2 emissions in the total values are based on market standards.
*2 Scope 1 emissions other than energy related CO₂ are excluded because their ratio to the total is very small.
*3 The use of gasoline in company vehicles is also included in the scope of calculation from FY2022.
Targets
In our long-term management vision "NETUREN VISION 2030," we have set a target of "30% reduction of CO₂ emissions by 2030 (compared to fiscal 2013) and virtually zero emissions by 2050." Each plant and office is taking the lead in reducing CO₂ emissions under the company-wide promotion system to achieve the target.
Material Flow
